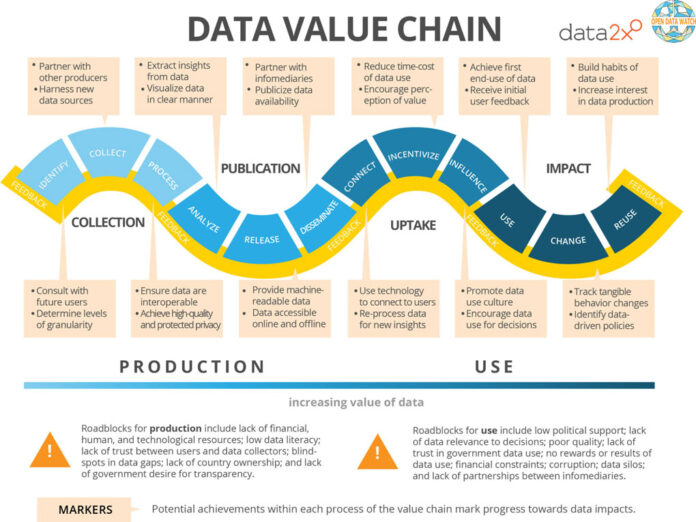
In today’s data-driven world, it’s not enough to just “know SQL” or “build dashboards.” To become a true modern data expert, you need to understand the full data value chain—from how raw data enters a system to how it powers decisions at the highest level.
Let’s walk through the five stages of the data value chain and explore how you can level up at each stage.
1. Data Collection: Build with Purpose
Modern data experts start with intentionality. It’s not just about gathering more data—it’s about gathering the right data.
- ✅ Best Practices:
- Work with product and operations teams to instrument clean data at the source.
- Ensure metadata, ownership, and context are defined from the beginning.
- Avoid data hoarding—ask why you’re collecting each field.
💡 Tip: Always think downstream—what questions will this data help answer?
2. Data Engineering: Architect for the Future
Gone are the days of batch ETL scripts duct-taped together. Modern experts embrace modular, scalable, and observable data pipelines.
- ✅ Best Practices:
- Embrace dimensional modeling and star schemas for analytical workloads.
- Use coverage tables for sparse data and bridge tables for complexity.
- Optimize for “getting data out”, not just getting it in.
💡 Tip: Understand both ETL and ELT, and know when each is appropriate.
3. Data Management: Govern Without Friction
Data management is more than governance—it’s about creating trust and usability without slowing teams down.
- ✅ Best Practices:
- Maintain conformed dimensions across domains.
- Implement SCD (slowly changing dimensions) appropriately.
- Build data catalogs and lineage tools that empower, not hinder.
💡 Tip: Make data discoverable, explainable, and safe—automate validation and testing.
4. Data Analysis: Tell the Story, Not Just the Stats
Analysts and scientists should do more than summarize—they should drive insight and action.
- ✅ Best Practices:
- Focus on data storytelling—use visuals, context, and narrative.
- Embrace negative data and outliers as learning tools.
- Think in frameworks: correlation ≠ causation, segmentation, cohorts, baselines.
💡 Tip: Communicate insights in the language of the business, not SQL.
5. Data Impact: Drive Strategic Decisions
At the top of the value chain is business impact. This is where data professionals become strategic partners.
- ✅ Best Practices:
- Map analysis to company OKRs and KPIs.
- Encourage a culture of data imagination, not just information.
- Align with stakeholders to co-own data questions, reducing resistance.
💡 Tip: The best data experts make others feel smart—they simplify, not mystify.
💡 Final Thoughts
To become a modern data expert, you need to zoom out from individual tools and focus on the full lifecycle of data—its journey from collection to strategic action. Mastering the 5-stage data value chain is your roadmap.
You’re not just a technician. You’re an architect, a translator, and a catalyst for change. Embrace that role.
🎯 THEME MAPPING BLOG ARTICLES ACROSS THE 5-STAGE DATA VALUE CHAIN
1. Get Data
Theme: Ingestion Efficiency, Format Optimization, and System Design
Key Ideas:
- Ingestion at Scale: Use
COPY INTOfor stable, batched loads;cloudFilesandwriteStreamfor streaming ingestion. - Efficiency: Use formats like Parquet, Avro, and compression (Snappy, GZip). Skip parsing issues with CSV.
- Delta Engine: Caching, data skipping (Bloom filters), Z-ordering, partitioning.
- Streaming: Emphasize event time, not processing time.
- Security: Tokenization, encryption, filtering.
- Data transport: Co-locate compute & data (Kubernetes), minimize transport costs.
- Formats: JSON (flexible), Avro (schema & compression), Parquet (columnar).
Data Example:
regex_extract()+ Spark DataFrame shows how you extract structured insight from raw log files.
2. Get Metadata
Theme: Trust, Governance, and Semantic Richness
Key Ideas:
- Metadata Enrichment: Schema, lineage, security, scale.
- Governance Principles: Unified governance for data + AI, open connectivity.
- Storage Optimization: Compaction, clustering, columnar storage.
- Data Contracts: Define schema, metadata, and change process.
- Tools: SKOS (Semantic Knowledge Org System), CUDOS for academic data rigor.
- Observability: Know data owners, coverage, usage, redundancy.
Data Example:
- Federated compute governance must handle metadata from different sources (schema, lineage, etc.).
3. Combine Data & Metadata (Knowledge Graphs)
Theme: Context, Semantic Federation, and Integrated Architecture
Key Ideas:
- Knowledge Graphs: Join structured data + metadata + semantics to form context-aware graphs.
- Linked Data: Enables semantic querying and insight generation.
- Data Fabric: Metadata semantic layer sits between sources and visualization.
- Federation: Tools like Starburst enable queries without data movement.
- Bounded Contexts: Align language and schema within each domain.
Data Example:
ksqluse with Kafka shows structured context-aware query building using metadata (e.g.,users_materialized.sql).
4. Add Semantics & Analyze (KX)
Theme: Intelligence, Transformation, and Insight
Key Ideas:
- ELT/Analytic Engineering: Transformation responsibility shifts from engineers to analysts.
- Big Data Techniques: Semantic analysis, association field discovery, NLP with spaCy.
- Statistical Rigor: Understand distributions, scatter/spread, mean reliability.
- Data Contracts vs. Observed Reality: Enables reactive, not brittle systems.
- Data Science Engineering: Blend statistics + engineering; use tools like DuckDB.
Data Example:
- Use of
spaCyfor NER + entity extraction connects raw data to semantic structures for downstream analysis.
5. Understand & Apply Principles (Wisdom)
Theme: Storytelling, Culture, and Strategic Impact
Key Ideas:
- Data Fluency: Data needs interpretation, narrative, and emotional connection.
- Storytelling Frameworks: Situation → Complication → Resolution.
- Trust-Building: Use insight for credibility (e.g., pay raise case, stakeholder buy-in).
- Decision-Making: Data + instinct. Data doesn’t eliminate risk.
- Culture: Democratize access, eliminate gatekeeping.
- Communication: Speech writing for data: purpose, three key facts, story, impact.
Data Example:
- Storytelling recipe using three datasets:
- Dataset 1 = Situation
- Dataset 2 = Problem
- Dataset 3 = Solution
🔄 Summary Table of Themes
| Stage | Core Theme | Supporting Example/Concepts |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Get Data | Efficiency, Streaming, Formats | Delta Engine, COPY INTO, cloudFiles, streaming with event time |
| 2. Get Metadata | Governance, Observability, Optimization | Data contracts, lineage, federated metadata, SKOS, data ownership |
| 3. Data + Metadata → Context | Semantic Fusion & Federation | Knowledge Graphs, Starburst, Linked Data, Data Fabric, Bounded Contexts |
| 4. Add Semantics → Knowledge | Insight Extraction & Semantic Analysis | NLP (spaCy), statistical insight, analytic engineering, transformation pipelines |
| 5. Apply Principles → Wisdom | Storytelling, Trust, Decision Impact | Situation-complication-resolution stories, humanized data, culture & fluency |